**Affiliate Disclosure**
Please note that some of the links on this site are affiliate links, and at no additional cost to you, we may earn a commission if you decide to make a purchase after clicking through the link. Any commission we make is income for the work put into supplying the information presented on this website.
Joint Replacement
Seniors are often faced with the choice of seeking out joint replacement surgery. This is due to the increased risk of bone and joint degeneration and the subsequent development of arthritis in many senior individuals.
While not all circumstances are appropriate reasons for surgery, seniors can greatly benefit from surgical treatment of the joints. Yet, it’s also important to understand that surgery always has associated risks and these issues must be considered and discussed with your doctor.
In what follows, we’ll be discussing several of the most common joint replacement surgeries that are possible for consideration in the senior population. Further, we’ll explore potential complications as well as satisfaction rates among those who pursue such treatment.
Joint Replacement Surgery
Joint replacement surgery is a common procedure for seniors who are experiencing pain and limited mobility due to degenerative joint conditions such as osteoarthritis. Surgery should only be pursued, however, when all other treatment options, such as medications or conservative management, have been exhausted.
The goal of joint replacement surgery is to reduce pain, improve mobility, and restore function to the affected joint. Joint replacement surgery is usually recommended for people who have severe pain and limited mobility due to degenerative joint conditions such as osteoarthritis (OA), rheumatoid arthritis (RA), or traumatic joint injury.
The procedure is usually performed under general anesthesia, which means the individual is put to sleep during the surgery. The surgery typically takes a few hours to complete, depending on the specific type of joint being surgically treated.
After the surgery, the individual will often need to stay in the hospital for a short period to recover, and extensive rest and physical therapy will follow discharge from the hospital setting.
Timelines for full recovery depend on several factors, including the type of surgery, size of the joint, age, and resilience of the individual; however, six weeks to 3 months is a standard range of time noted for this type of procedure.
Types of Joint Replacement
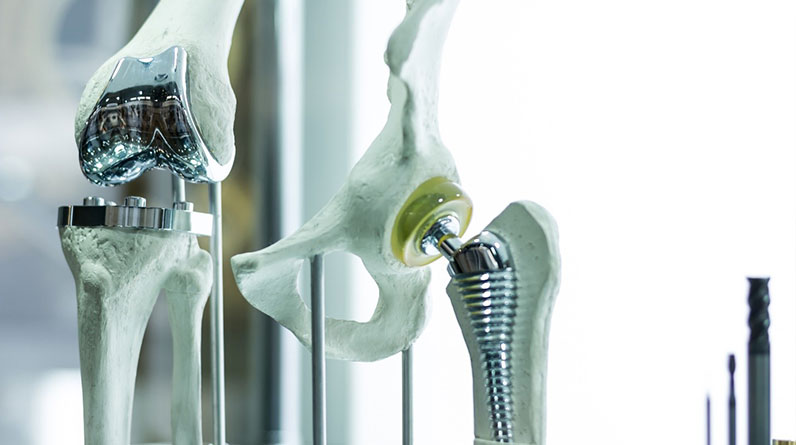
There are several types of joint replacement surgeries that are commonly performed, including knee replacement, hip replacement, shoulder replacement, and elbow replacement.
The following is a discussion of these different procedures that details their prevalence rates, potential complications, and satisfaction rates.
Knee Replacement
Knee replacement surgery, also known as total knee arthroplasty, is one of the most common types of joint replacement surgeries in seniors.
It involves replacing the damaged or worn-out parts of the knee joint with artificial components, such as a metal or plastic femoral component, a tibial component, and a polyethylene patellar component.
Knee replacement surgery is usually recommended for individuals who have severe knee pain and limited mobility due to advanced osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis (RA), or other degenerative joint conditions.
The success rate of knee surgery is around 85% ten years out from surgery, particularly in patients with RA.
Hip Replacement
Otherwise known as total hip arthroplasty, hip replacement surgery is another common type of joint replacement surgery, often performed in seniors.
It involves replacing the damaged or worn-out parts of the hip joint with artificial components, such as a metal or ceramic femoral component and a plastic or ceramic acetabular component. The acetabulum is part of the hip joint.
Hip replacement surgery is usually recommended for those experiencing severe hip pain that prevents them from being able to walk due to conditions such as RA, advanced osteoarthritis, or other degenerative joint conditions.
The success rates of hip surgery have dramatically improved since its inception, now showing a 90-95% success rate after 10-20 years.
Shoulder Replacement
Shoulder replacement surgery, otherwise known as total shoulder arthroplasty, is a less common but popular type of joint replacement surgery in individuals.
It involves replacing the damaged parts of the shoulder joint with artificial components, such as a metal or plastic humeral head component and a plastic or ceramic glenoid component. The glenoid region is part of the shoulder joint.
Shoulder replacement surgery is usually recommended for those who have incapacitating shoulder pain that can be secondary to osteoarthritis, RA, or other degenerative joint conditions.
Elbow Replacement
Elbow replacement surgery, also known as total elbow arthroplasty, is rarely performed but has been shown to be an effective surgical option for seniors who have severe elbow pain and limited mobility. The causes of this pain can be secondary to a previous injury, advanced osteoarthritis, or other degenerative joint conditions.
The surgical procedure involves replacing the affected areas of the elbow joint with artificial components, such as described previously.
Final Thoughts
Joint replacement surgery can be an effective treatment option for seniors who are experiencing pain and limited mobility. However, like any surgery, joint replacement surgery carries a risk of potential complications, such as infection, bleeding, or nerve damage.
Satisfaction rates for joint replacement surgery vary depending on the specific type of joint and the individual’s health condition. In general, most seniors who undergo joint replacement surgery report significant improvement in their pain levels and mobility after the procedure.
